Analyzing US Inflation Trends and Federal Reserve Rate Projections
In September, the US inflation rate ticked up to 3.0% year-over-year, prompting discussions about the Federal Reserve’s next moves in interest rates. As the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reported a vulnerable increase of 0.3% for the month, the core CPI remained stable at 3.0%. Key contributors to inflation included a 4.1% rise in gasoline prices, while shelter inflation remained around 3.6%. Despite the backdrop of a potential government shutdown, the Bureau of Labor Statistics fulfilled its timeline for Social Security cost-of-living adjustments, underscoring the complexity of the current economic landscape.
Market reactions indicate traders are largely undeterred by the CPI report. Data from CME Group’s FedWatch tool highlights an over 90% probability of a 25 basis point rate cut during the upcoming Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting on October 29. This could adjust the federal funds target rate from the current range of 3.75% to 4.00% down to 3.50% to 3.75%. Looking ahead, FedWatch projects that the funds rate might settle around 3% by this time next year, indicating a gradual easing of monetary policy.
The projections for interest rates extend to the October 2026 meeting, where the probabilities suggest a target range of 2.75% to 3.25%. Analysts anticipate multiple rate cuts in 2025 and 2026, positioning the funds rate within the 3.00% to 3.25% range by late 2026, according to Goldman Sachs. Furthermore, monetary policy rules from the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland indicate a high-3s policy rate for the same timeframe, suggesting that persistent inflation could maintain rates above what market futures imply.
The nuances of interest rate movements are further informed by analysis of yield curves. Two-year treasury yields linger around 3.4% to 3.5%, while the yield on 10-year treasury bonds hovers near 4%. The behavior of long-term treasury yields may signal how easily financial conditions could shift in response to interest rate adjustments. While some analysts predict the long end of the yield curve will stabilize around 4.1% to 4.2% over the next year, other factors, including term premiums and fiscal supply, could keep these rates elevated.
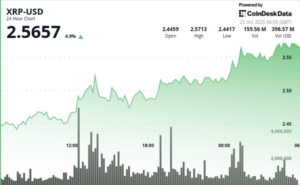
In the realm of digital assets, the connection between monetary policy and market behavior remains significant. For instance, Bitcoin experienced substantial inflows into crypto exchange-traded products (ETPs), amounting to a record $5.95 billion in early October coinciding with a surge in prices. However, following a turbulent period that included macroeconomic announcements, particularly regarding tariffs on China, the market saw considerable outflows. Spot Bitcoin has since consolidated between $108,000 to $111,000 as traders look towards upcoming CPI and FOMC decisions.
As the FOMC meeting approaches, the market anticipates a 25 basis point cut in interest rates, along with cautious guidance from the Federal Reserve. If this forecast aligns with reality, it would likely loosen monetary conditions in the short term while maintaining the 10-year yield near 4%. Various future scenarios emerge as we look to October 2026. They include a path of gradual disinflation that could stabilize core inflation near 3%, alongside scenarios of sticky inflation that may keep the Fed on guard. Another potential outcome could be a growth scare leading to more aggressive rate cuts.
Finally, the relationship between global economic conditions, European Central Bank policies, and other international factors will continue to influence the dollar and overall market sentiments. With significant macroeconomic indicators indicating imminent decisions by the Fed, traders and investors alike remain vigilant for new data that could shape future expectations. The next FOMC meeting will serve as a critical juncture for both inflation rates and interest rate policies as the Fed weighs its options in a landscape marked by persistent economic challenges.